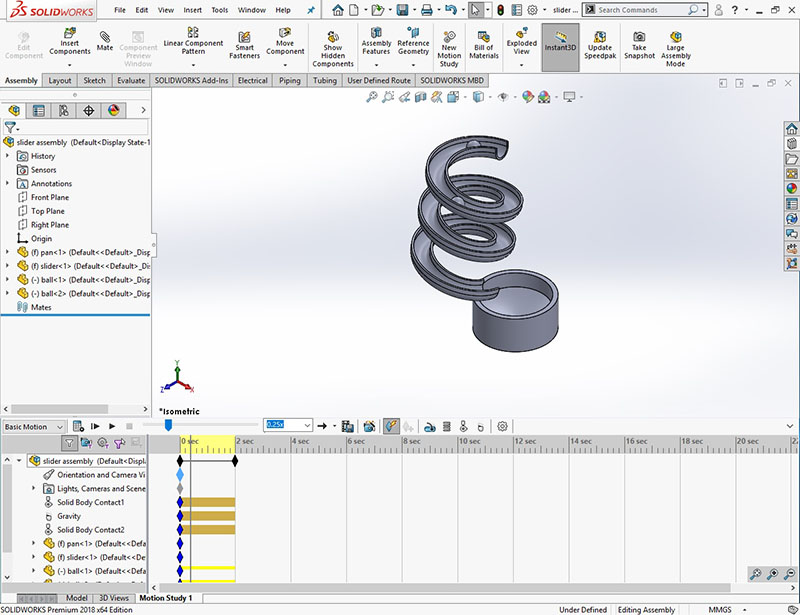
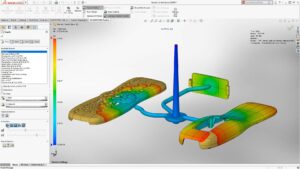
You can use Motion Analysis (available with the SOLIDWORKS Motion add-in from SOLIDWORKS Premium) to accurately simulate and analyze the motion of an assembly while incorporating the effects of Motion Study elements (including forces, springs, dampers, and friction).
Gravity (Basic Motion and Motion Analysis only) is a simulation element that moves components around an assembly by inserting a simulated gravitational force.
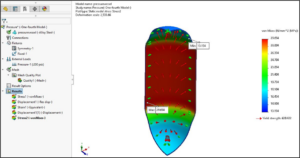
Gravitational Motion Analysis in SOLIDWORKS with Gravity property
In SOLIDWORKS, the Gravity Property Manager applies linear accelerations to a part or assembly document for use in structural and nonlinear analyses.
You specify accelerations in the x, y, and z directions of a coordinate system defined by a reference plane or planar face. You can also define linear acceleration along a straight edge.
Gravity loading in each direction is calculated by multiplying the specified acceleration of gravity by the mass. The mass is calculated from the density value of the material. If you select a material from a default library, then the density is already defined. If you choose to input material properties manually, make sure to specify the density. Distributed and remote masses are considered for the supported analysis types.
For nonlinear studies, you can define time-dependent accelerations of gravity.
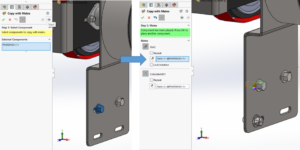
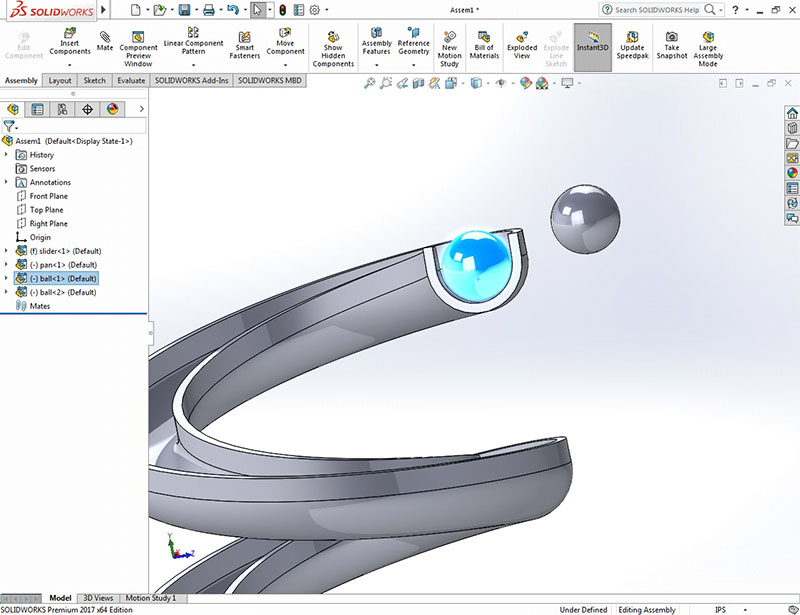
- Insert Existing Components (Slider, Ball and Bowl) in Assembly Design and place properly (Don’t Mate any parts, just place).
- For duplicate component press Ctrl and drag that part.
- Fix the Bowl.
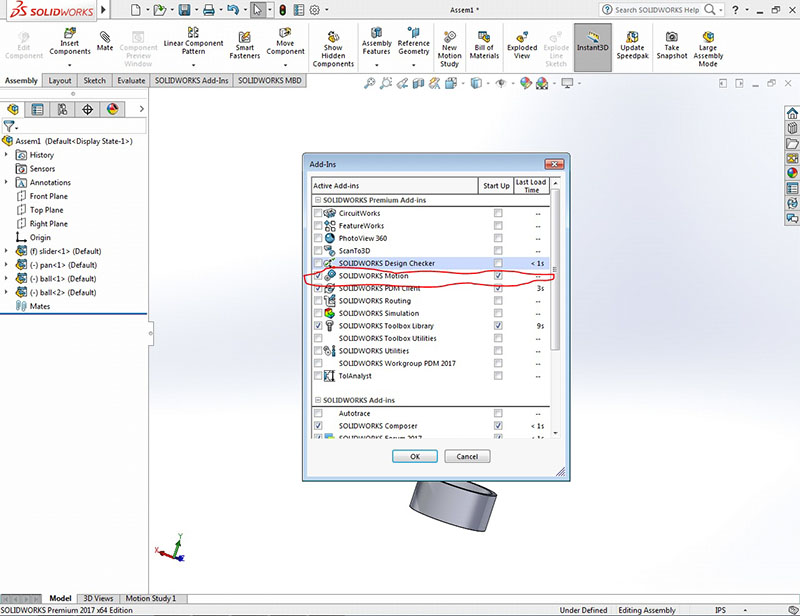
For Motion Analysis we have to add SOLIDWORKS Motion
- Add-ins
- Mark SOLIDWORKS MOTION (Both box)
Choose Motion Analysis option for motion study
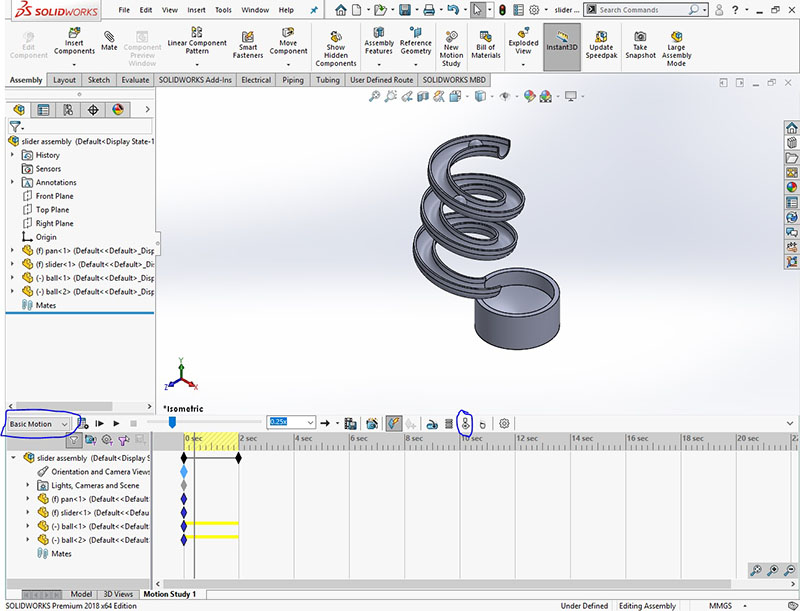
- Apply the CONTACT (marked in the image) option to all the parts.

2. For gravitational motion study we have to apply gravitational force to the part.
Select one edge for directional reference (Optional).
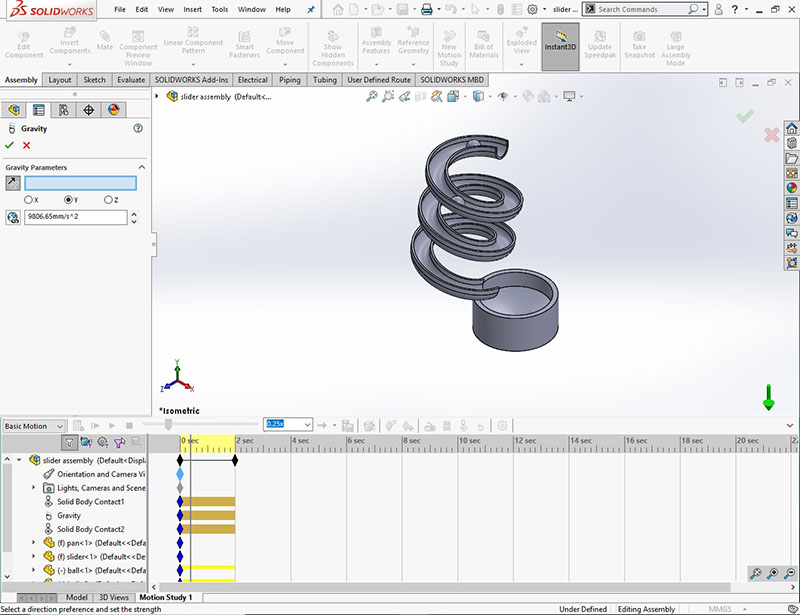
3. Now calculate Motion Analysis by clicking calculate.